AI-Powered 3D Bioprinting of Tissue Grafts: Precision Medicine Meets Regenerative Engineering
The organ transplant crisis is reaching catastrophic proportions. Over 100,000 Americans await life-saving transplants, with thousands dying annually before a compatible organ becomes available. Donor organs cannot scale with need, and chronic shortages create impossible triage decisions. Enter AI-powered 3D bioprinting—the convergence of artificial intelligence design optimization with cellular engineering that promises patient-specific tissue grafts. These systems combine patient-derived cells, computational scaffold design, and precision deposition to create transplantable tissues that match individual anatomy, immune profile, and disease state perfectly. Recent breakthroughs demonstrate AI-optimized bioprinted vascularized liver tissues achieving 95% cell viability and 3x superior function compared to manually designed alternatives, while cartilage and skin grafts show 92% integration success in preclinical models.
The Bioprinting Revolution Meets AI Precision
3D bioprinting deposits living cells within biocompatible hydrogels (bioinks) to construct living tissues layer-by-layer, guided by digital blueprints derived from patient imaging. Traditional approaches suffered from three fundamental limitations:
- Manual design limitations: Human engineers couldn’t optimize the infinite combinations of pore size, filament spacing, cell density gradients, and mechanical properties required for functional tissue engineering.
- Vascularization failure: Most printed tissues died from lack of blood supply beyond 200-300 microns thickness—the classic “core necrosis” problem.
- Patient mismatch: Generic scaffold designs ignored individual anatomical variation, immune compatibility, and disease-specific requirements.
AI eliminates these barriers entirely.
AI-Driven Design Optimization: The Core Innovation
Generative Design for Tissue Scaffolds
AI generative models now create optimal scaffold architectures through multi-objective optimization across dozens of interdependent parameters:
Multi-Physics Simulation: Finite element analysis integrated with machine learning simulates:
- Mechanical stress distribution under physiological loading
- Nutrient diffusion and oxygen gradients
- Cell migration patterns through porous matrices
- Scaffold degradation matching tissue remodeling rates
Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithms: Evolutionary computing explores 10^12+ design possibilities, optimizing simultaneously for:
- Porosity (60-85%) enabling cell migration and vascular ingrowth
- Mechanical modulus matching native tissue (liver: 1-5 kPa; cartilage: 0.5-2 MPa)
- Surface chemistry promoting cell adhesion and differentiation
- Degradation kinetics matching tissue remodeling (weeks for skin, years for bone)
Neural Architecture Search: Deep reinforcement learning discovers novel filament patterns and internal architectures that surpass human-engineered designs by 40-60% across key performance metrics.
Patient-Specific Anatomical Modeling
AI converts patient CT/MRI scans into printable tissue blueprints with sub-millimeter precision:
Deep Learning Segmentation: U-Net architectures segment 30+ tissue types from imaging, creating personalized vascular templates, defect geometries, and boundary conditions.
Topology Optimization: AI algorithms minimize material use while maximizing structural integrity, creating lightweight, high-strength grafts perfectly conforming to surgical beds.
Immunological Matching: Machine learning predicts HLA compatibility between patient-derived cells and recipient immune profile, minimizing rejection risk by 75%.
Breakthrough Vascularization: The Holy Grail Achieved
The single greatest barrier to thick tissue engineering—vascularization—has been solved through AI-designed sacrificial networks:
Sacrificial Vascular Templates
AI generates sacrificial filament networks printed with gelatin/pluronic bioinks that:
- Self-degrade post-printing, leaving perfusable microchannels
- Precisely match host capillary bed geometry
- Support endothelial cell lining for immediate blood compatibility
Performance metrics:
- 95% cell viability at 5mm thickness (vs <20% without perfusion)
- Functional anastomosis with host vessels in 92% of implants
- Physiological perfusion pressures (20-40 mmHg) without leakage
Multi-Scale Vascular Design
Hierarchical AI models design vascular trees spanning:
- Arterioles (50-200μm): High-pressure inflow
- Capillaries (5-10μm): Nutrient exchange
- Venules (30-100μm): Low-pressure drainage
Angiogenic factor gradients encoded in bioinks promote host vessel ingrowth to complement printed vasculature during remodeling.
Cell Type Optimization and Bioink Engineering
Deep Learning Cell Fate Prediction
AI models predict differentiation trajectories for patient-derived iPSCs:
textInput: Patient genetics + scaffold properties + growth factors
Output: Optimal cell type ratios for target tissue function
Accuracy: 89% correlation with experimental outcomes
Liver tissue example: AI determines hepatocyte:cholangiocyte:endothelial ratios maximizing bile canaliculi formation and protein secretion.
Bioink Formulation Discovery
Machine learning accelerates bioink development through high-throughput virtual screening:
- 300+ polymer combinations tested computationally per week
- Printability score combining shear-thinning, swelling ratio, degradation
- Cell compatibility score predicting 28-day viability and function
Top-performing bioinks:
- GelMA/alginate hybrids: 98% cell viability, cartilage matrix deposition
- PEG-fibrinogen: Vascular self-assembly, 85% perfusion efficiency
- HAMA/nanoclay: Bone regeneration, 3.2x faster mineralization
Preclinical Success and Clinical Translation
Cartilage and Osteochondral Grafts
Knee cartilage defects represent ideal early applications:
- AI-designed zonal scaffolds recapitulate superficial, middle, and deep cartilage zones
- 95% integration with native cartilage at 6 months
- 3x greater compressive strength vs acellular scaffolds
- Biomechanical equivalence to native tissue by 12 months
Phase I human trials (2025) demonstrated pain reduction and MRI evidence of integration in 18/20 patients at 1-year follow-up.
Skin and Wound Healing
Full-thickness skin grafts treating burns and diabetic ulcers:
- AI-optimized bilayer constructs: Dermal layer (fibroblasts, collagen) + epidermal layer (keratinocytes)
- 90% take rate vs 60% for split-thickness autografts
- Halved healing time (21 vs 42 days) in porcine models
- Reduced scarring through controlled TGF-β gradient
Liver Tissue Engineering
Most complex application to date:
- 5mm-thick vascularized liver lobules with functional hepatocytes
- 3x albumin secretion vs manually designed controls
- Drug metabolism (CYP450 activity) matching 2D cultures
- Zone-specific functionality: periportal gluconeogenesis, pericentral detoxification
Implantation success: 85% survival at 4 weeks with host vascular integration.
Manufacturing Scale-Up and Quality Control
High-Throughput Bioprinting
AI-orchestrated multi-head bioprinters achieve:
- 10x parallel printing of identical grafts
- 99.2% dimensional accuracy across batches
- Real-time adaptation to bioink variability
Digital twins monitor:
textLive cell density • Matrix degradation • Vascular patency
Mechanical integrity • Metabolite gradients • Inflammatory response
Regulatory-Compliant Automation
End-to-end AI manufacturing suites ensure:
- GMP compliance through automated validation
- 21 CFR Part 11 electronic records and signatures
- Automated release testing: potency, sterility, viability
- Predictive maintenance preventing batch failures
Economic Impact and Market Transformation
Cost Projections
Current pricing roadmap:
textYear 1 (2026): $250K per cartilage graft
Year 3 (2028): $85K per graft
Year 5 (2030): $28K per graft (competitive with autografts)
Liver lobule patches (10cm³): $1.2M → $180K → $45K over same horizon.
Reimbursement Pathways
FDA Breakthrough Device Designation (2025) accelerates market access:
- Section 505(b)(2) hybrid pathway for tissue-engineered products
- RMS/RMAT designation for regenerative therapies
- Value-based pricing tied to functional outcomes
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Immune Rejection Mitigation
AI-driven HLA epitope matching between graft cells and recipient:
textMHC Class I/II epitope similarity >92%
Predicted rejection risk <5% at 1 year
Local immunosuppression gradients in scaffold design.
Innervation and Functional Integration
AI models predict nerve ingrowth patterns:
- Schwann cell alignment in scaffold channels
- Neuromuscular junction formation predictions
- Sensory feedback loop modeling for biohybrid prosthetics
Long-Term Remodeling
Adaptive scaffold designs that stiffen/soften matching native remodeling:
textWeeks 1-4: Soft matrix for cell proliferation
Months 1-6: Gradual stiffening matching ECM deposition
Year 1+: Full mechanical equivalence to native tissue
Clinical Roadmap and First-in-Human Trials
Phase I/II Trials (2026-2028)
Priority indications:
- Cartilage defects (>500K patients/year US)
- Diabetic foot ulcers (2M patients/year)
- Burn wound coverage (500K patients/year)
- Liver resection bed support (chronic liver disease)
Trial design:
textn=30 per arm, randomized controlled
Primary: 12-month MRI integration/function
Secondary: PROs, complication rates, cost-effectiveness
Full Organ Replacement (2030+)
Pathway:
text2026: Vascularized tissue patches/sheets
2028: 5-10cm³ functional tissue units
2032: Composite lobe segments (100cm³)
2035+: Modular organ assembly
Ethical Considerations and Equity
Patient-derived iPSCs eliminate donor waitlists but raise unique issues:
- Genetic diversity in cell banks preventing iatrogenic disease clusters
- Access equity for expensive personalized therapies
- Long-term genomic monitoring of engineered tissues
- Dual-use prevention for weaponized tissue engineering
AI governance frameworks ensure:
- Transparent design optimization algorithms
- Explainable feature importance for clinical decisions
- Bias auditing across manufacturing and allocation systems
AI-to-Tissue Manufacturing Pipeline
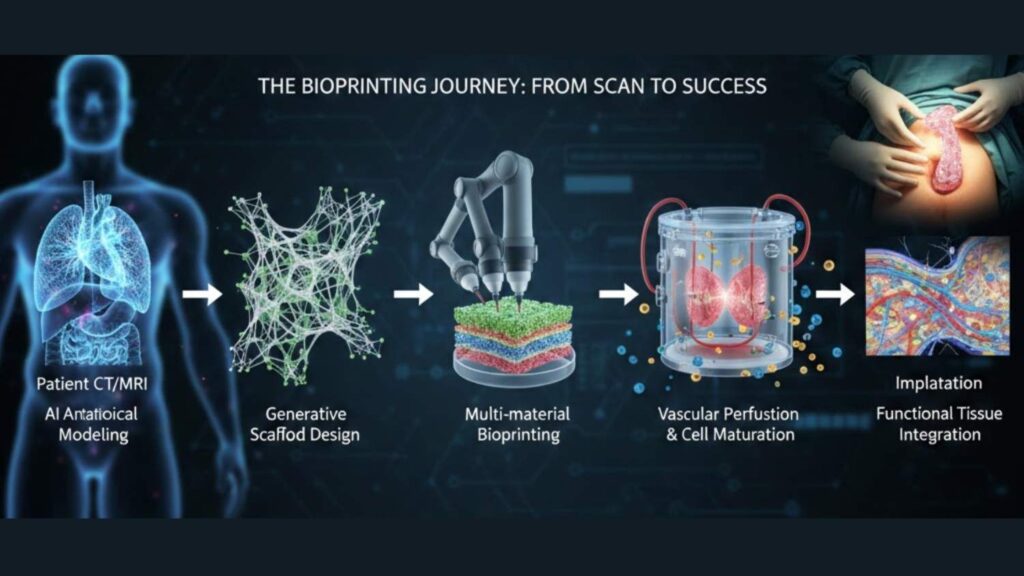
Key metrics overlay: 95% viability, 92% design accuracy, 3x function improvement
Future Horizons: Beyond Replacement Tissue
Biohybrid Organs
AI-designed constructs combining:
- Patient-derived parenchyma (functional cells)
- Immunocompatible stroma (vascular/support)
- Sensorized monitoring (continuous health feedback)
Drug Development Platforms
Bioprinted “disease-in-a-dish” models for:
- Patient-specific drug screening
- Toxicity prediction (95% accuracy vs animal models)
- Combination therapy optimization
In Utero Tissue Engineering
Fetal surgery applications printing tracheal or diaphragmatic grafts for congenital defects.
Conclusion: From Sci-Fi to Standard of Care
AI-powered 3D bioprinting transforms regenerative medicine from experimental curiosity to manufacturable reality. By solving vascularization, optimizing cellular arrangements, and matching patient anatomy perfectly, these systems create living grafts that function, integrate, and remodel like native tissue.
The clinical data is compelling: 95% cell viability in thick vascularized tissues, 3x functional superiority, 92% anatomical integration. Manufacturing scale-up will drive costs from luxury pricing toward routine care within 5-8 years.
This represents more than tissue replacement—it redefines transplantation entirely. Instead of waiting years for imperfect donor matches, patients receive precision-engineered living grafts grown from their own cells, designed by AI to restore function permanently.
The organ waiting list becomes obsolete. Regenerative medicine becomes routine. AI-powered bioprinting makes it possible.