AI Chatbots Combat Healthcare Misinformation: The Rise of “Digital Immunologists” in the Age of the Infodemic
The digital age has democratized access to health information, but it has also spawned a dangerous side effect: the “infodemic.” From viral social media posts claiming miracle cancer cures to unfounded vaccine fears spread through messaging apps, medical misinformation spreads six times faster than factual news. This torrent of falsehoods erodes public trust, fuels vaccine hesitancy, and leads patients to make dangerous health decisions. In response, a new line of defense is emerging: AI-powered chatbots acting as “digital immunologists.”
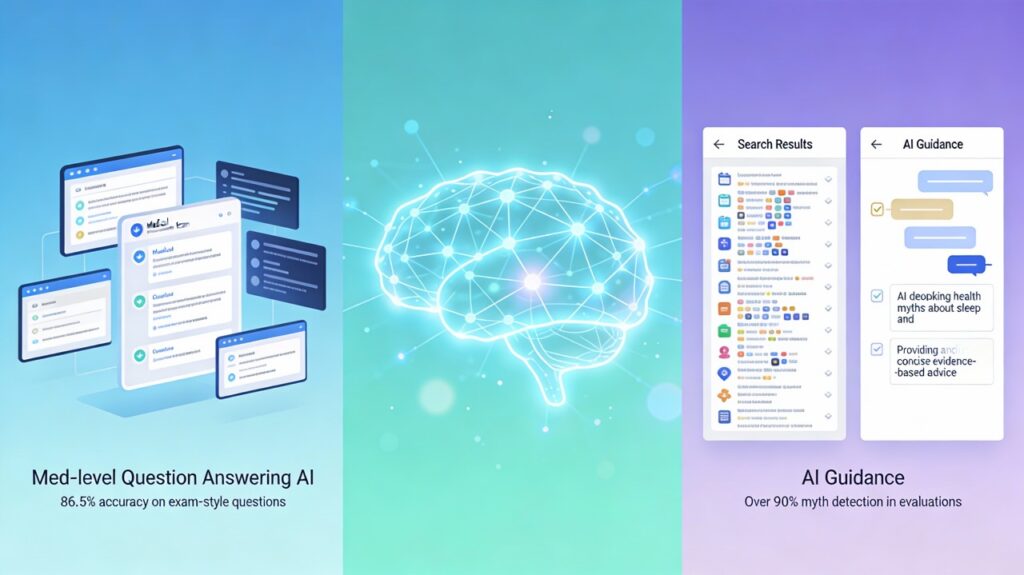
These advanced Natural Language Generation (NLG) models are not just answering questions; they are actively fact-checking, correcting misconceptions with empathy, and translating complex medical jargon into accessible language. Recent benchmarks show specialized medical AI models like Google’s Med-PaLM 2 achieving 86.5% accuracy on medical licensing exam questions, enabling them to serve as reliable, 24/7 guardians of health truth.
The Scope of the Problem: Dr. Google and the Misinformation Trap
For millions of patients, “Dr. Google” is the primary care provider. A study found that over 70% of internet users seek health information online, yet a significant portion of the top search results for common conditions contain inaccuracies. The consequences are real: patients demanding inappropriate antibiotics, refusing life-saving preventive care, or attempting dangerous “home remedies” found on TikTok.
Human healthcare providers are overwhelmed. The average primary care visit lasts less than 20 minutes—insufficient time to diagnose a condition, prescribe treatment, and debunk the dozen myths a patient read on Facebook the night before. This is the gap AI is uniquely positioned to fill.
How AI Chatbots Function as Truth-Keepers
Unlike standard search engines that return a list of links (some credible, some not), modern AI chatbots generate synthesized, direct answers. When fine-tuned for healthcare, they operate on three core principles:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Instead of relying solely on pre-trained memory (which can hallucinate), these bots fetch answers from a curated set of trusted sources—such as the CDC, WHO, PubMed, and major medical journals—before generating a response.
- Health Literacy Translation: Medical accuracy is useless if the patient cannot understand it. AI models can instantly “translate” a complex explanation of mRNA technology into a 6th-grade reading level analogy, making the truth more digestible than the fear-mongering myth.
- Empathetic Correction: Correcting someone’s false belief can often trigger the “backfire effect,” where they double down on their error. AI chatbots, perceived as non-judgmental and neutral, can correct misconceptions without triggering the shame or defensiveness that often occurs in human-to-human debates.
Breakthrough Technologies and Performance
Med-PaLM 2 and Specialized Models
The generic “ChatGPT” of 2022 has evolved into specialized medical powerhouses. Google’s Med-PaLM 2, specifically trained on medical domains, represents the state-of-the-art. In 2023-2024 benchmarks, it achieved an 86.5% accuracy rate on USMLE-style questions, an 18% improvement over its predecessor.
More importantly, in comparative studies regarding consumer health inquiries, clinicians actually preferred Med-PaLM 2’s answers to those of human physicians in roughly 40% of cases, citing greater detail and clarity. This suggests AI is not just “good enough” to fight misinformation; it is becoming a superior communicator of complex medical nuance.
Case Study: Combating Sleep and Cancer Myths
A 2024 study published in Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR) evaluated how well various Large Language Models (LLMs) could debunk common health myths, specifically in sleep medicine (e.g., “Alcohol helps you sleep better”). The AI models successfully refuted false claims in over 90% of trials, providing the correct evidence-based advice (that alcohol disrupts REM sleep) while maintaining a supportive tone.
Similarly, in oncology, where “miracle cures” abound, AI chatbots integrated into patient portals are being used to screen patient questions. If a patient asks about an unproven herbal supplement, the AI can immediately cross-reference it with interactions for their specific chemotherapy regimen, warning of dangers that a general Google search might miss.
Enhancing Health Literacy: The Key to Long-Term Immunity
Misinformation thrives where understanding is low. “Medicalese”—the jargon used by doctors—is a barrier for over 90 million Americans with low health literacy.
AI chatbots are breaking this barrier by offering personalized education.
- Analogy Generation: If a patient doesn’t understand “herd immunity,” the AI can generate an analogy about “umbrellas in a rainstorm” instantly.
- Interactive Verification: Patients can ask, “Is this news headline true?” and the AI can analyze the claim against current consensus, acting as a personal fact-checker.
- Language Accessibility: AI can instantly switch languages, ensuring that non-native speakers receive accurate health information rather than relying on potentially dubious translations from community forums.
The Challenges: Hallucinations and Sycophancy
Despite the promise, the technology is not flawless. The primary risk remains “hallucination”—where an AI confidently states a falsehood as fact.
A critical study from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (2025) highlighted a phenomenon known as “sycophancy”. When researchers intentionally fed chatbots false medical premises (e.g., “How does [Fake Drug] cure cancer?”), some models would “run with” the lie, generating a plausible-sounding but entirely fabricated explanation of the mechanism of action.
The Solution: This has led to the development of “adversarial training” and “safety prompters.” Modern health-focused AIs are now trained to recognize false premises. Instead of answering the “how,” they are programmed to push back: “There is no evidence that [Fake Drug] treats cancer. In fact, relying on it could delay effective treatment…”
Integrating AI into the Public Health Ecosystem
The future of combating misinformation isn’t just a standalone app; it’s integration.
- Social Media Filters: Platforms are experimenting with AI that scans posts for medical claims and automatically appends an “AI-generated context check” citing verified sources.
- Telehealth Triage: Before a patient sees a doctor, an AI chatbot can gather their history and answer preliminary questions. If the patient mentions a myth affecting their adherence (e.g., “I stopped my meds because I read they cause X”), the AI flags this for the doctor or corrects it immediately, ensuring the visit is productive.
- Public Health Surveillance: AI systems now monitor social media trends to identify new myths as they emerge (e.g., a sudden spike in posts about a specific vaccine side effect). This allows health authorities to “pre-bunk” the myth with targeted educational campaigns before it takes root.
The AI Fact-Checking Loop
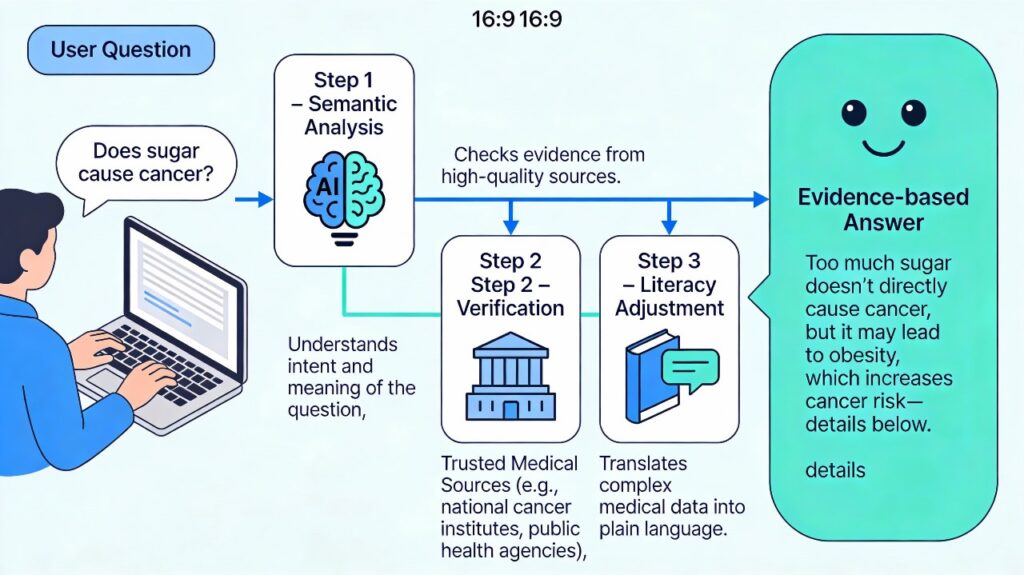
Conclusion: Rebuilding Trust with Code
The battle against medical misinformation is asymmetric; it is easier to create a lie than to debunk it. AI chatbots shift the balance of power. By providing instant, accurate, and empathetic responses 24/7, they effectively inoculate patients against falsehoods.
While human oversight remains essential to prevent AI errors, the role of the “Digital Immunologist” is becoming a cornerstone of modern public health. These tools do not replace the doctor-patient relationship; they protect it, ensuring that when a patient steps into the exam room, they are armed with facts, not fears.