Wearable ECG Monitors: Your Personal Heart Health Assistant
Introduction: The Heart Health Revolution at Your Wrist
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death globally, claiming approximately 20.5 million lives annually. Yet, what if you could detect potential cardiac issues before they become life-threatening? Welcome to the era of wearable ECG monitors – sophisticated devices that transform how we monitor, understand, and protect our heart health. These pocket-sized guardians are revolutionizing cardiovascular care by bringing medical-grade heart monitoring directly to consumers.
From smartwatches that detect atrial fibrillation to chest patches providing continuous 14-day monitoring, wearable ECG devices are no longer futuristic concepts – they’re essential health tools available today. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about choosing, using, and benefiting from these remarkable personal heart health assistants.

Smartwatch displaying heart rate and ECG graph with a reading of 62 bpm
Understanding Wearable ECG Technology: Beyond Simple Heart Rate Monitoring
What Makes ECG Monitoring Different?
Unlike traditional heart rate monitors that measure pulse through photoplethysmography (PPG), ECG monitors capture the actual electrical signals produced by your heart’s contractions. This fundamental difference enables detection of rhythm irregularities that basic pulse monitoring might miss entirely.
An electrocardiogram measures the heart’s electrical activity through sensors that detect voltage changes across heart muscle tissue. While a clinical 12-lead ECG provides comprehensive cardiac assessment, wearable devices typically use single-lead or limited-lead configurations optimized for detecting specific conditions like atrial fibrillation.
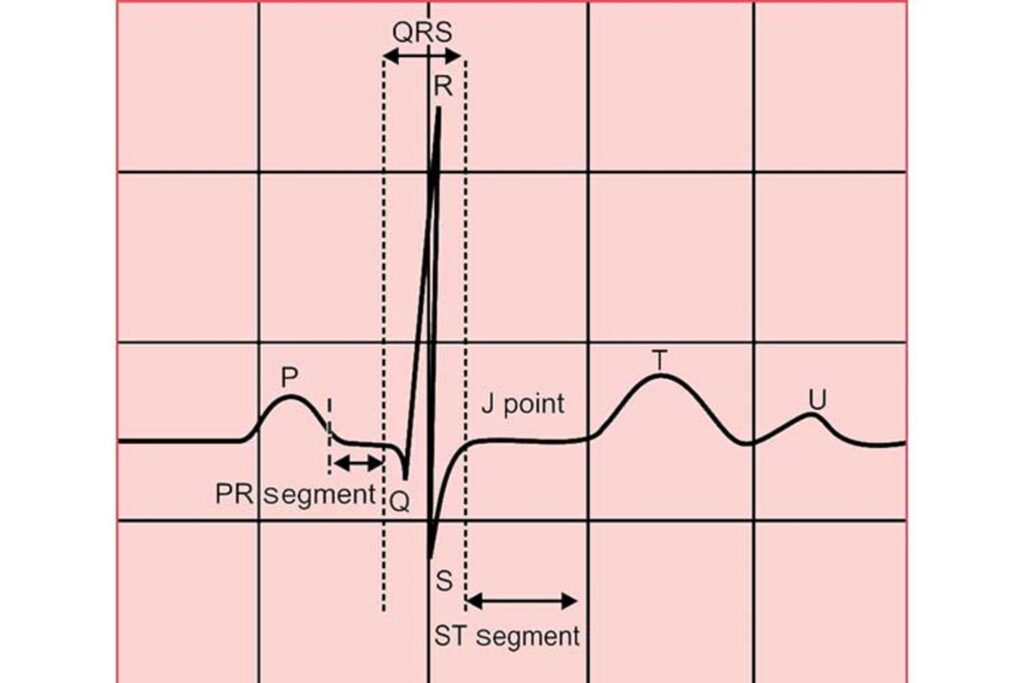
Labeled ECG waveform showing the P wave, QRS complex, T and U waves, and key segments relevant to cardiac monitoring
How Wearable ECG Devices Work
Modern wearable ECG monitors employ several sophisticated technologies:
Electrode-Based Detection: Devices like the Apple Watch Series 4 and later use electrodes built into the watch case and Digital Crown. When you place your finger on the crown, it completes an electrical circuit that captures heart rhythm data.
Chest-Mounted Sensors: Professional-grade devices like the Frontier X2 use chest placement for optimal signal quality, providing continuous monitoring during all activities including sleep and exercise.
Patch-Based Systems: Advanced patches like the Zio monitor offer extended wear periods up to 14 days, capturing intermittent arrhythmias that shorter monitoring periods might miss.
Wearable ECG monitor device displaying heart rhythm and usage scenarios on wrists and abdomen
The Science Behind Accuracy: Clinical Validation and FDA Approval
FDA-Cleared Devices Lead the Market
The FDA has approved several consumer wearable ECG devices for medical use, establishing their credibility for health monitoring:
- Apple Watch Series 4 and later: First smartwatch to receive FDA clearance for ECG functionality
- Samsung Galaxy Watch series: Approved for rhythm monitoring with 88% sensitivity and 81% specificity for atrial fibrillation detection
- Fitbit Sense 2: CE-marked and FDA-cleared for heart rhythm assessment
- Withings ScanWatch: European clearance for ECG monitoring capabilities
Clinical Accuracy Studies
Recent research demonstrates impressive accuracy across leading devices. A comprehensive study comparing Apple, Samsung, and Withings smartwatches found that Apple and Samsung devices achieved 87-88% sensitivity and 81-86% specificity for automated atrial fibrillation detection. Expert interpretation improved accuracy further, with sensitivity reaching 94-96% for Apple and Withings devices.
For chest-based monitors, accuracy approaches clinical-grade standards. The Polar H10 chest strap achieved 99% concordance with clinical ECG measurements, while wrist-worn devices like the Apple Watch demonstrated 80% concordance under controlled conditions.
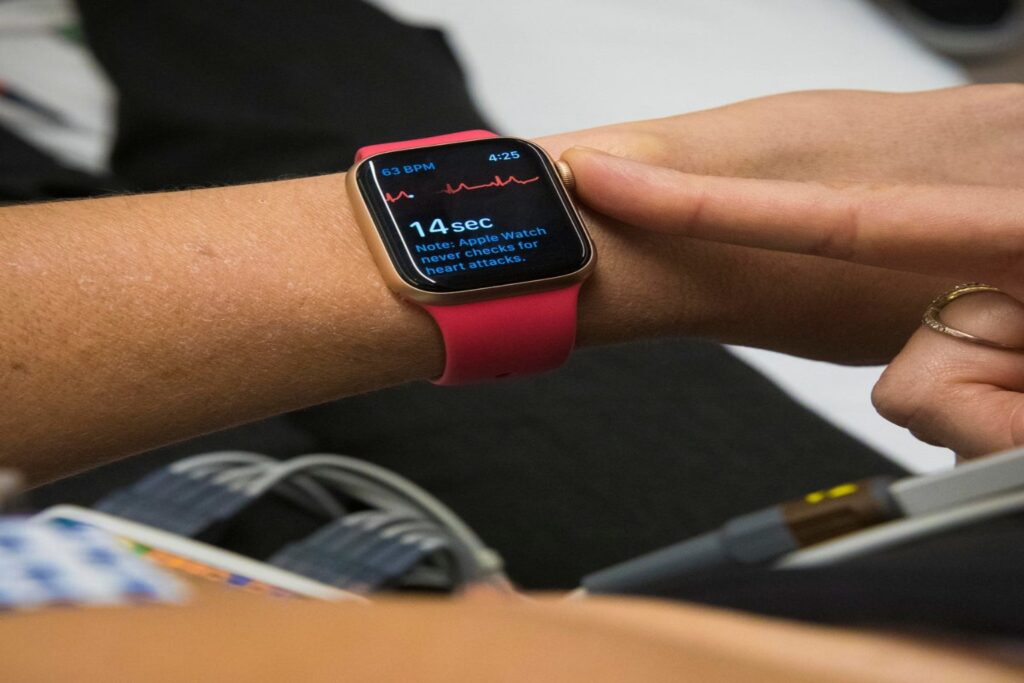

Apple Watch displaying ECG monitoring with heart rate and waveform
Market Growth and Consumer Adoption: A Booming Industry
The wearable ECG monitor market is experiencing explosive growth, reflecting increasing consumer awareness of heart health importance. Market analysis reveals remarkable expansion projections:
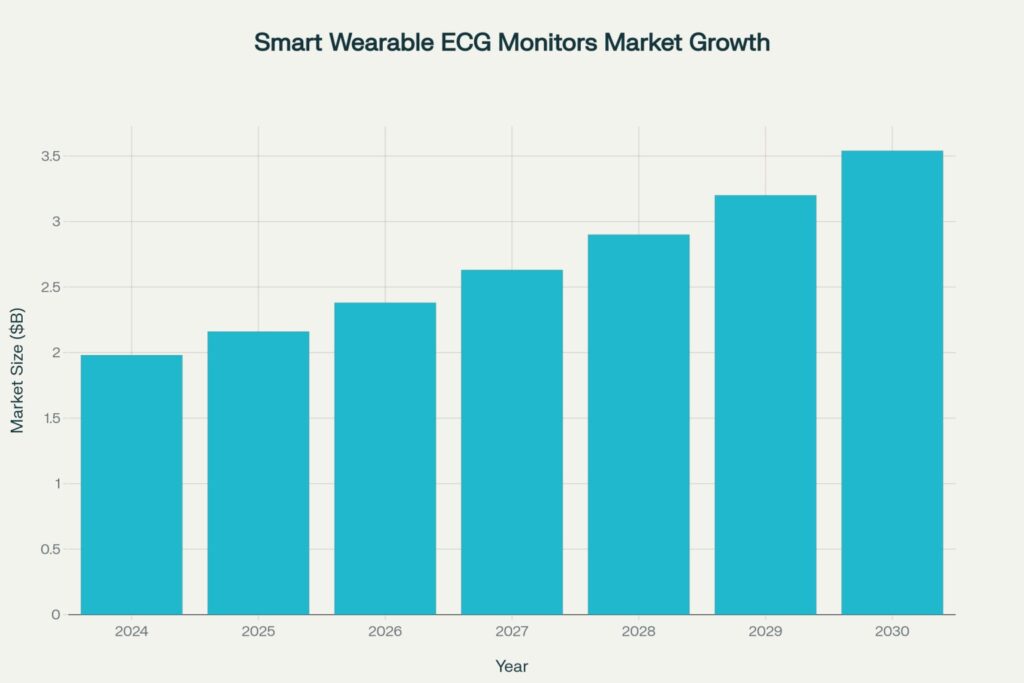
Smart Wearable ECG Monitors Market Growth projecting significant expansion from $1.98B in 2024 to $3.54B by 2030
This growth trajectory, representing a compound annual growth rate of 10.33% from 2025 to 2030, is driven by several key factors:
- Aging Population: Increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases among older adults
- Technology Advancement: Improved sensor accuracy and battery life
- Healthcare Cost Reduction: Preventive monitoring reduces expensive emergency interventions
- Consumer Health Awareness: Growing emphasis on proactive health management
Key Market Drivers
The cardiovascular device market encompasses broader trends beyond simple consumer adoption. Professional healthcare integration is accelerating, with hospitals and clinics incorporating wearable data into patient care protocols. Insurance companies increasingly recognize the value of preventive monitoring, with some offering premium discounts for users of approved monitoring devices.
Types of Wearable ECG Monitors: Finding Your Perfect Match
Smartwatch-Integrated ECG
Modern smartwatches represent the most accessible entry point into ECG monitoring. Leading options include:
Apple Watch Series 9/10 and Ultra models offer seamless iOS integration with automatic irregular rhythm notifications. The device can detect atrial fibrillation with 87% sensitivity and 97% specificity when worn continuously.
Samsung Galaxy Watch 8 and Ultra provide comprehensive health tracking with ECG functionality requiring Samsung smartphone compatibility. Recent models include advanced sleep monitoring and stress detection capabilities.
Fitbit Sense 2 combines ECG monitoring with stress management tools and detailed sleep analysis, making it ideal for holistic health tracking.
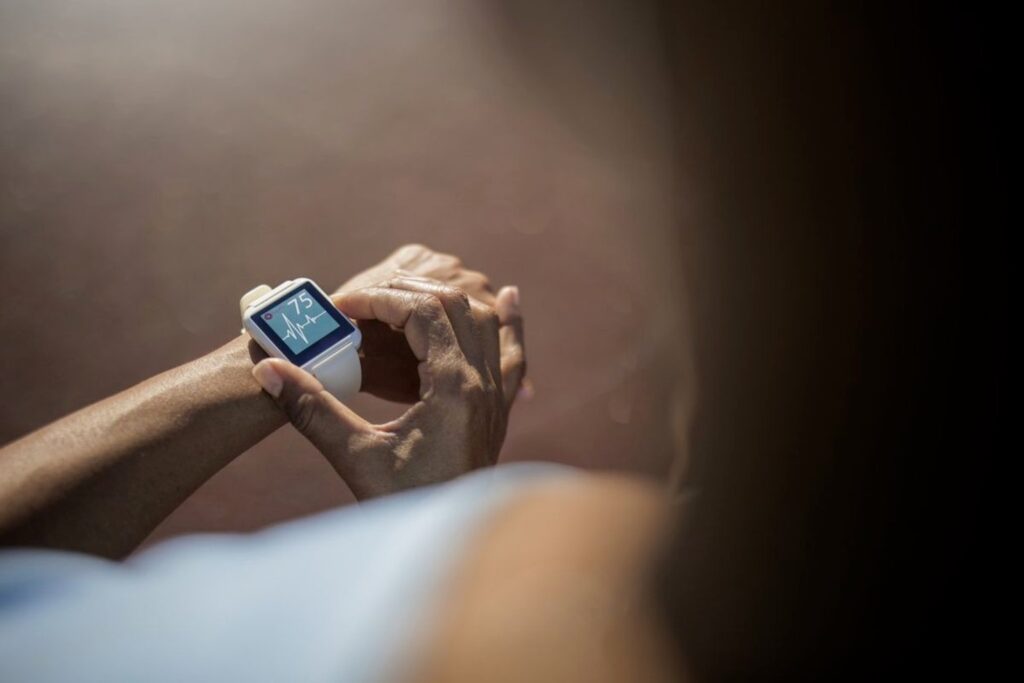

A person checking their heart rate and ECG reading on a white smartwatch, demonstrating wearable heart health monitoring technology
Dedicated Handheld Devices
For users prioritizing medical-grade accuracy over continuous monitoring, handheld devices offer superior precision:
KardiaMobile 6L provides six-lead ECG readings in just 30 seconds, detecting atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, and tachycardia with clinical accuracy. The device connects via Bluetooth to smartphones and stores unlimited recordings.
Omron Complete Wireless Monitor combines ECG functionality with blood pressure measurement, offering comprehensive cardiovascular assessment in a single device.
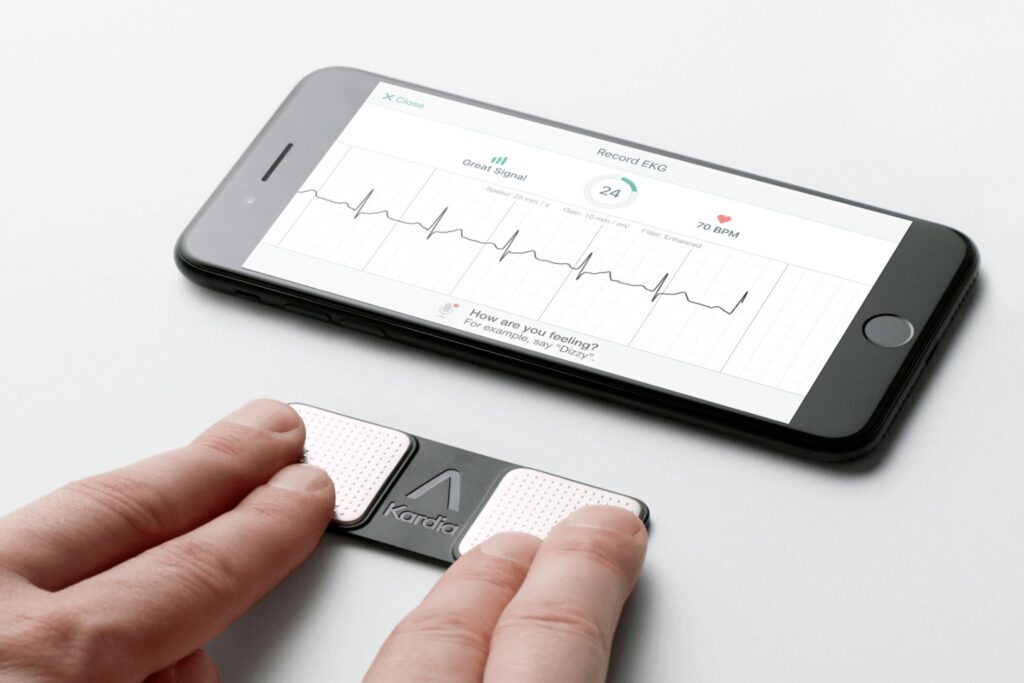
KardiaMobile portable handheld ECG device captures real-time heart activity and displays the EKG waveform on a smartphone app
Chest-Mounted Continuous Monitors
For serious athletes and patients requiring 24/7 monitoring, chest-mounted devices provide unparalleled accuracy:
Frontier X2 offers continuous ECG monitoring during 20+ activities, measuring heart rate variability, VO2 max, and cardiovascular strain with research-grade precision.
Polar H10 serves as the gold standard for exercise ECG monitoring, achieving 99% accuracy compared to clinical equipment while maintaining comfort during extended wear.
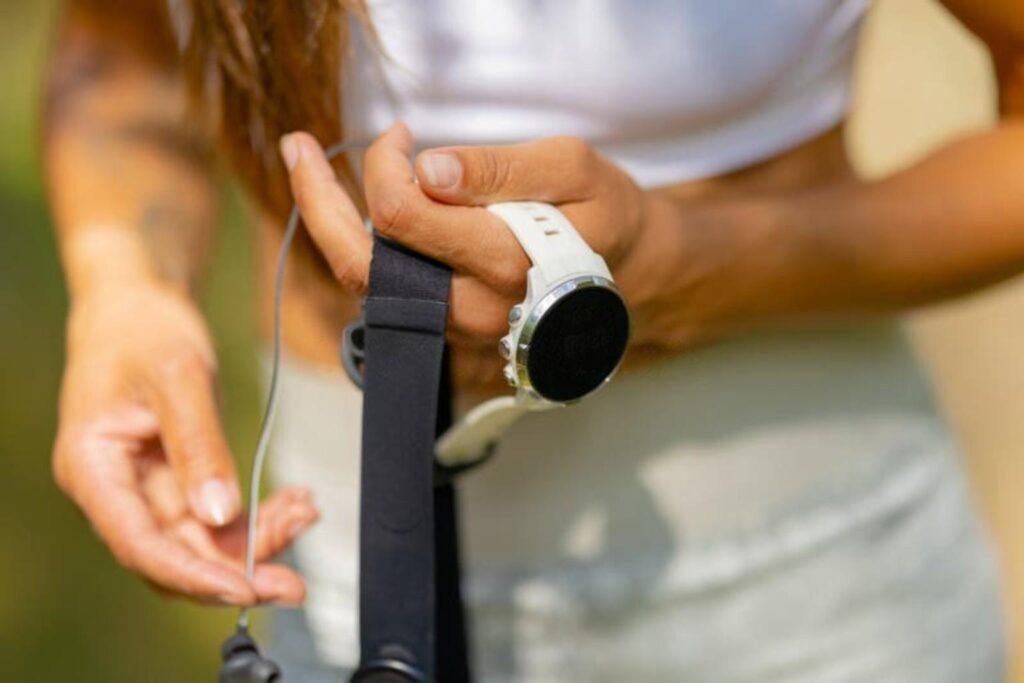

Woman holding a chest strap heart rate monitor while wearing a white fitness smartwatch for personal heart health tracking
Long-Term Monitoring Patches
For clinical diagnostic purposes, extended-wear patches bridge the gap between consumer devices and hospital monitoring:
Zio Patch by iRhythm provides up to 14 days of continuous monitoring with waterproof design and automatic arrhythmia detection. Studies show 63.2% diagnostic yield compared to traditional 24-hour Holter monitors.
CardioTag by Cardiosense combines ECG, photoplethysmogram, and seismocardiogram signals for comprehensive cardiac function assessment, recently receiving FDA clearance.
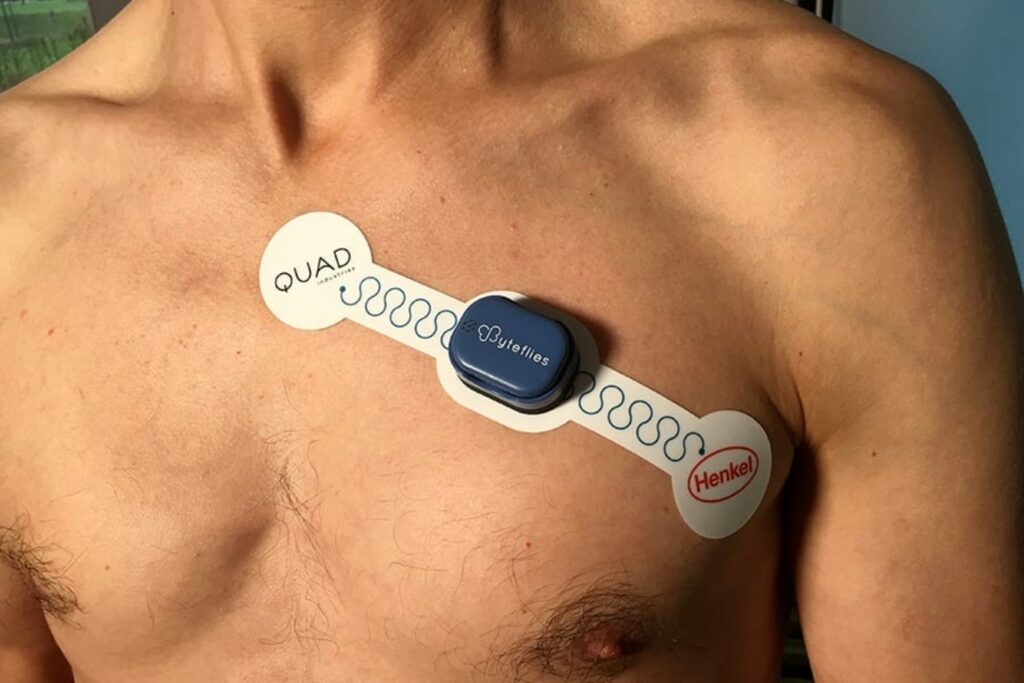
Wearable ECG chest patch monitor by Quad Industries and Henkel with a compact sensor device for personal heart health tracking
Health Benefits: Beyond Heart Rate Tracking
Early Detection of Serious Conditions
Wearable ECG monitors excel at detecting conditions that might otherwise go unnoticed:
Atrial Fibrillation Screening: The most validated application, with studies showing consumer devices can identify silent AF in 1.5-6.7% of screened populations. Early detection enables anticoagulation therapy that prevents strokes.
Heart Rate Variability Assessment: Advanced devices measure HRV to assess autonomic nervous system balance, stress levels, and recovery status – valuable for both athletes and individuals managing chronic conditions.
Arrhythmia Documentation: Captures intermittent irregular rhythms that traditional monitoring might miss, providing crucial diagnostic information for cardiologists.
Lifestyle and Fitness Optimization
Beyond medical diagnosis, wearable ECG monitors enhance daily health management:
Exercise Zone Training: Precise heart rate monitoring enables optimal training intensity, maximizing cardiovascular benefits while avoiding overexertion.
Sleep Quality Assessment: Some devices monitor heart rate patterns during sleep to assess sleep quality and identify potential sleep-disordered breathing.
Stress Management: Real-time heart rate variability feedback helps users recognize and manage stress responses throughout the day.
Chronic Disease Management
For individuals with existing cardiovascular conditions, wearable monitors provide valuable ongoing surveillance:
Medication Monitoring: Track heart rate responses to cardiac medications, enabling precise dosage optimization.
Symptom Correlation: Record ECG during symptoms like palpitations or chest discomfort, providing objective data for healthcare providers.
Recovery Tracking: Monitor heart rate patterns during cardiac rehabilitation or post-surgical recovery periods.
Accuracy and Limitations: Setting Realistic Expectations
Understanding Device Limitations
While wearable ECG monitors offer remarkable capabilities, users must understand their limitations:
Single-Lead Limitations: Most consumer devices provide single-lead ECG data, offering less comprehensive information than clinical 12-lead systems. This limits detection of certain conditions like bundle branch blocks or left ventricular hypertrophy.
Motion Artifacts: Wrist-worn devices are susceptible to movement-related interference, potentially reducing accuracy during vigorous activity. Chest-mounted devices typically provide more stable signals.
Skin Contact Requirements: Proper electrode contact is essential for accurate readings. Factors like skin moisture, hair, and device positioning significantly impact signal quality.
Age and Health Factor Considerations
Research reveals that accuracy varies across different user populations:
Age-Related Accuracy: Wrist-worn monitors demonstrate reduced accuracy in younger patients, likely due to different vascular characteristics.
Medication Effects: Users taking diuretics may experience reduced monitor accuracy, possibly due to electrolyte changes affecting skin conductivity.
Skin Tone Considerations: While most studies show minimal impact, varying skin pigmentation may affect optical sensor performance in some devices.
False Positives and Anxiety Management
A significant concern with widespread ECG monitoring is the potential for false alarms. Studies indicate that 20% of users experience extreme anxiety when receiving irregular rhythm alerts. Healthcare providers recommend:
- Understanding normal heart rate variations
- Avoiding excessive monitoring behavior
- Consulting healthcare providers before making medication changes based on device readings
- Using devices as screening tools rather than diagnostic instruments
Choosing the Right Device: A Comprehensive Buying Guide
Assess Your Monitoring Goals
Before selecting a device, clearly define your objectives:
General Health Awareness: For basic heart health monitoring, smartwatch-integrated ECG provides convenient, occasional checking capabilities.
Athletic Performance: Serious athletes benefit from chest-mounted devices offering continuous, research-grade accuracy during training.
Medical Monitoring: Individuals with known cardiac conditions may require physician-prescribed extended monitoring devices.
Family History Concerns: Those with cardiovascular disease family history might prioritize devices with proven atrial fibrillation detection capabilities.
Key Features to Evaluate
Battery Life: Consider how monitoring frequency affects battery requirements. Smartwatches typically last 1-2 days with active ECG use, while dedicated devices may operate for weeks.
Connectivity Options: Ensure compatibility with your smartphone ecosystem. Some devices require specific operating systems or manufacturer apps.
Data Storage and Sharing: Evaluate how easily you can store, review, and share ECG data with healthcare providers. Cloud storage and PDF export capabilities are valuable features.
Comfort and Wearability: For continuous monitoring, device comfort becomes crucial. Consider factors like weight, strap materials, and waterproof ratings.
Regulatory Approval: Prioritize FDA-cleared or CE-marked devices for medical applications, ensuring clinical validation and safety standards.
Budget Considerations
Wearable ECG devices span a wide price range:
Entry Level ($50-150): Basic handheld devices like KardiaMobile provide essential ECG functionality without continuous monitoring.
Mid-Range ($200-400): Consumer smartwatches with ECG capabilities offer balanced functionality for general health monitoring.
Professional Grade ($400-800): Advanced chest monitors and medical-grade devices provide research-quality data for serious applications.
Clinical Systems ($800+): Extended-wear patches and professional monitoring systems designed for healthcare provider use.
Expert Recommendations: Top Picks for 2025
Best Overall: Apple Watch Series 10
The Apple Watch Series 10 represents the pinnacle of consumer ECG technology, combining proven accuracy with seamless ecosystem integration. FDA-cleared for atrial fibrillation detection, it offers automatic irregular rhythm notifications and easy data sharing with healthcare providers.
Pros: Excellent accuracy, comprehensive health app ecosystem, automatic monitoring
Cons: Requires iPhone, limited battery life with active use
Best for Athletes: Frontier X2
For serious fitness enthusiasts and athletes, the Frontier X2 provides unmatched continuous monitoring capabilities. Its chest placement ensures optimal signal quality during all activities, while advanced analytics provide insights into cardiovascular strain and recovery.
Pros: Research-grade accuracy, 24/7 monitoring, comprehensive activity tracking
Cons: Higher price point, requires chest strap wear
Best Value: KardiaMobile 6L
The KardiaMobile 6L offers exceptional value for users seeking medical-grade ECG readings without continuous monitoring requirements. Its six-lead capability provides more comprehensive data than single-lead consumer devices.
Pros: Clinical accuracy, portable design, extensive smartphone compatibility
Cons: Manual activation required, no continuous monitoring
Best for Extended Monitoring: Zio Patch
For clinical diagnostic purposes, the Zio Patch provides unparalleled extended monitoring capabilities. Its 14-day wear period captures intermittent arrhythmias that shorter monitoring periods might miss.
Pros: Extended wear capability, waterproof design, automatic analysis
Cons: Prescription required, single-use device
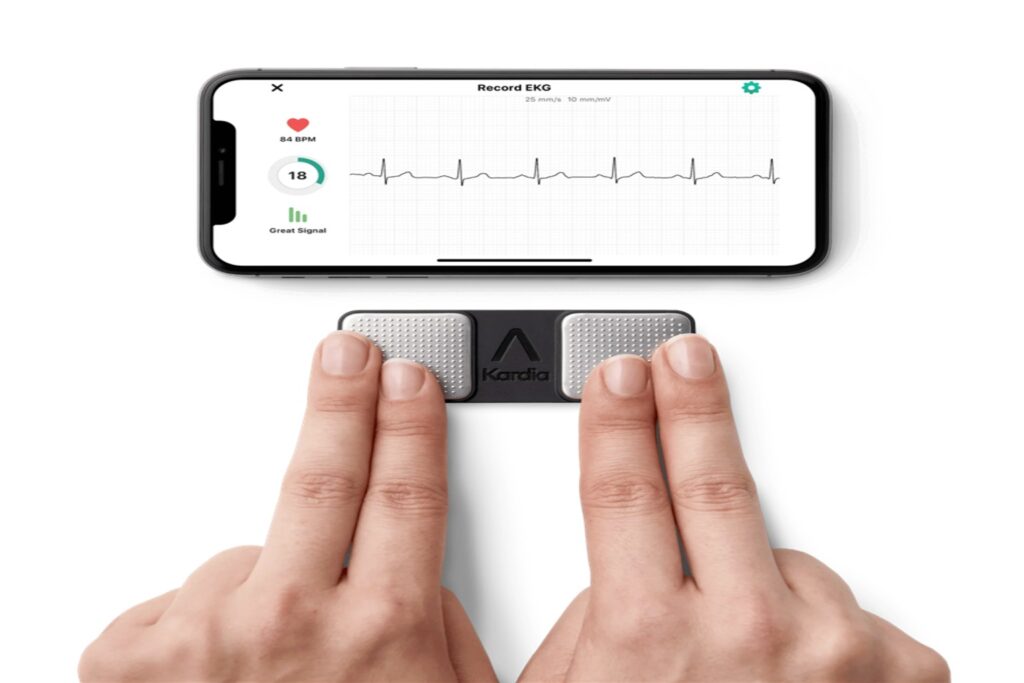
KardiaMobile handheld ECG monitor recording an EKG displayed on a smartphone app in real time, showcasing wearable heart health technology
Future Trends: The Evolution of Cardiac Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The integration of AI algorithms is revolutionizing ECG interpretation capabilities. Advanced machine learning models can now detect subtle patterns indicative of various cardiac conditions, potentially identifying issues before they become clinically apparent.
Predictive Analytics: Future devices will predict cardiac events based on pattern recognition, enabling preventive interventions.
Personalized Baselines: AI will establish individual normal ranges, improving abnormality detection accuracy.
Enhanced Sensor Technology
Emerging sensor technologies promise improved accuracy and expanded monitoring capabilities:
Multi-Modal Monitoring: Devices combining ECG, PPG, and seismocardiogram signals provide comprehensive cardiac assessment.
Flexible Electronics: Advanced materials enable more comfortable, skin-conforming sensors for extended wear.
Miniaturization: Continued size reduction makes devices increasingly unobtrusive and comfortable.
Healthcare System Integration
The future of wearable ECG monitoring lies in seamless healthcare integration:
Electronic Health Records: Direct integration with medical records streamlines patient care and enables better treatment decisions.
Telemedicine Platforms: Remote monitoring capabilities reduce healthcare costs while improving patient access to specialist care.
Population Health Analytics: Aggregated data from millions of users will provide insights into cardiovascular disease patterns and prevention strategies.
Getting Started: Implementation and Best Practices
Initial Setup and Configuration
Proper device setup ensures optimal performance and accurate readings:
Skin Preparation: Clean skin thoroughly before applying electrodes or wearing chest straps. Remove excessive body hair if necessary for proper contact.
Baseline Establishment: Take several readings during different times and activities to establish your personal baseline patterns.
App Configuration: Configure notification settings to avoid alarm fatigue while ensuring important alerts reach you promptly.
Developing Monitoring Habits
Effective ECG monitoring requires consistent, purposeful use:
Regular Rhythm Checks: Establish routine times for ECG readings, such as morning and evening, to track patterns over time.
Symptom Documentation: Record ECG readings whenever experiencing symptoms like palpitations, chest discomfort, or unusual fatigue.
Activity Correlation: Note activities, meals, medications, and stress levels when taking readings to identify potential triggers.
Data Management and Healthcare Provider Communication
Organize Your Data: Regularly review and organize ECG recordings, noting any concerning patterns or changes.
Prepare for Medical Appointments: Print or export relevant ECG data to share with healthcare providers during visits.
Understand Normal Variations: Learn to recognize normal heart rate variations due to activity, caffeine, sleep, and stress to avoid unnecessary anxiety.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
When to Seek Medical Attention
While wearable ECG monitors provide valuable health insights, certain situations require immediate medical evaluation:
Persistent Abnormal Readings: Multiple abnormal ECG readings over several days warrant healthcare provider consultation.
Symptoms with Abnormal ECG: Chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness accompanied by irregular ECG readings require prompt medical attention.
Significant Pattern Changes: Dramatic changes in baseline ECG patterns may indicate developing cardiac conditions.
Device Limitations and Medical Disclaimers
Not Diagnostic Tools: Remember that consumer ECG devices are screening tools, not replacements for professional medical diagnosis.
Emergency Limitations: Do not rely on wearable devices during medical emergencies. Call emergency services for acute symptoms.
Medication Interactions: Some medications may affect heart rhythm patterns. Discuss device use with healthcare providers when starting new medications.
Conclusion: Embracing Your Personal Heart Health Assistant
Wearable ECG monitors represent a revolutionary advancement in personal health management, offering unprecedented access to cardiac monitoring capabilities previously available only in medical settings. From detecting silent atrial fibrillation to optimizing athletic performance, these devices provide valuable insights that can genuinely improve health outcomes and save lives.
The key to successful implementation lies in understanding both the capabilities and limitations of these technologies. Choose devices that match your specific needs, establish consistent monitoring habits, and maintain open communication with healthcare providers about your findings.
As the technology continues advancing with AI integration, improved sensors, and enhanced healthcare system connectivity, wearable ECG monitors will become even more powerful tools for preventive cardiac care. The future of heart health monitoring is not in distant medical facilities – it’s right on your wrist, in your pocket, or discretely monitoring from your chest, serving as your personal cardiovascular guardian 24/7.
Whether you’re managing existing cardiac conditions, optimizing athletic performance, or simply taking proactive steps toward better heart health, wearable ECG monitors offer an accessible, accurate, and empowering approach to cardiovascular wellness. The question isn’t whether to embrace this technology – it’s which device will best serve as your personal heart health assistant.